This article discusses the question of poverty eradication efforts in Malaysia especially in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Incidence of poverty by state and ethnic wise in percentage are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Malaysias economic growth and transformation from the 1970s have involved profound changes including generally improved material well-being that involves upward social mobility for much of the population.

. In other words eradicating poverty is more important for improving the health of Malaysians than building more hospitals or training more doctors. They point out that the income threshold used for the poverty linecurrently a monthly household income of 510 ringgit US134 in western peninsular. The ability to eradicate poverty is the single biggest predictor of good health.
Concepts like press freedom and conservation may not matter as much when one is poor and struggling to survive. Science technology and innovation need to be the way forward for Malaysia and Malaysians. The increase in absolute poverty in Malaysia is caused by the direct and indirect economic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Recent report published by DOSM 2020 reveals an increase in the incidence of absolute poverty from 56 in 2019 to 84 in 2020. A Unicef survey in December 2020 called Families on. In Malaysia life expectancy has improved significantly over the last few decades from 70.
1The latest available statistics from 2015 show that Malaysia has higher life expectancy than the world average 7166 yr as well as higher life expectancy than some developing countries in the region such as Indonesia 6907 yr. Are shown in Table 1 and Table 2 economic disparity in Malaysia increased 53. Before the pandemic Malaysia was performing relatively well as absolute poverty.
But critical analysts complain that this figure is misleading. In Malaysia there are three concepts of poverty that we are able to adopt. Despite Malaysia having achieved some commendable results in eradicating poverty over the decades today the country is witnessing increased poverty and inequality in both rural and urban areas.
A constant improvement of its micro economy Department of Statistics Malaysia 2011. In 2016 it had a population of 31187265. As we kick off the month that saw Malaya gaining its independence 64 years ago the release of Malaysias Voluntary National Review VNR.
Malaysian poverty is a real problem. Reports often point to the fall in absolute poverty levels in Malaysiafrom 29 percent in 1980 to about 5-6 percent in 2000. The Ministry of Economic Affairs recently said the PLI which is used to measure absolute poverty is based on a households basic requirements to live healthily and actively.
Yr in 1990 to 7487 yr in 2015 Fig. An important component of the fight against poverty in Malaysia was the agreement on the definition and measurement of poverty. Life expectancy went up by almost two years from 2002 to 2015 and it has a reputation for the massive strides it has made in poverty reduction due to its economic growth.
Relative poverty and urbanization in Malaysia increased to 53 per cent in May it on. Malaysia is a country located on the Malay Peninsula in southeast Asia. Poverty in Malaysia is a controversial economic issue.
Statement poverty that is often referred in Malaysia is absolute poverty because the household income is compared with the PGK N orzita et al 2014. The overall poverty rate is 37 in Malaysia Department of Statistics Malaysia 2011. Reviews past and present trends of urbanization and urban poverty.
Finally the government of Malaysia should take greater measures to solve this issue as poverty and income inequality serves as a major limitation of economic development and growth. The impact of Covid-19 on Malaysias absolute poverty rate. Malaysia is no longer just grappling with absolute poverty but also with relative poverty pockets of persistent poverty and urban poverty as well as.
The definition of absolute poverty. The converse is also true that the single best predictor of poorer health is poverty. Socioeconomic indicators for basic amenities poverty health education occupations and real incomes all point to improved living standards for most.
Hardcore poverty was reduced from 12 in 2004 to 07 in 2009 and the incidence of overall poverty fell from 57 in 2004 to 38 in 2009. However rapid urbanization and industrialization is expected to bring in rural migrants into urban centres bringing along low incomes while putting pressure on urban services infrastructure and the environment. Beyond income levels and be more all-encompassing and multi-dimensional ethnic inequality and poverty in Malaysia that buried poverty issue in malaysia article Dewan.
Malaysia aspires to be a developed nation by 2020 and if these development ambitions are to be attained Malaysia needs to reexamine its past approaches to reducing poverty and inequalities in the country. Table 1 shows the Base Line Poverty Level PGK set up by the Economic Planning Unit for rural and urban area of Peninsular Malaysia Sabah and Sarawak. Citation neededMalaysias total population is 31 million as of 2015 of which 06 live below the national poverty line.
In 2021 Malaysias population is estimated to be. The incidence of poverty has been drastically reduced from 493 in 1970 to 38 in 2010 and hardcore poverty was nearly eradicated in 2009 1. Reports that urban poverty in Malaysia is not considered a serious phenomenon.
Rural poverty is greater compared to urban poverty. In the same year its GDP was 296359 billion. Absolute poverty absolute hardcore poverty and the relative poverty.
The definition of poverty and the poverty line for Malaysians has been disputed and government policies to address poverty such as the Malaysian New Economic Policy have been met with political protest. Malaysia currently uses a PLI level of RM980 nationally and at a higher level of RM1020 for Sarawak and RM1180 for Sabah to factor in additional costs. The Problem Of Poverty In Malaysia.
Aug 2 2021 130 PM. THE other day I.

Employment And Poverty Econofact

Stunting Is Preventable Unicef Children Stunts

To Move The Needle On Ending Extreme Poverty Focus On Rural Areas

Asean Outlook 2020 Part 2 Marketing Investing Fullerton

Malaysia Poverty Rate Of Rural And Urban Areas 2019 Statista
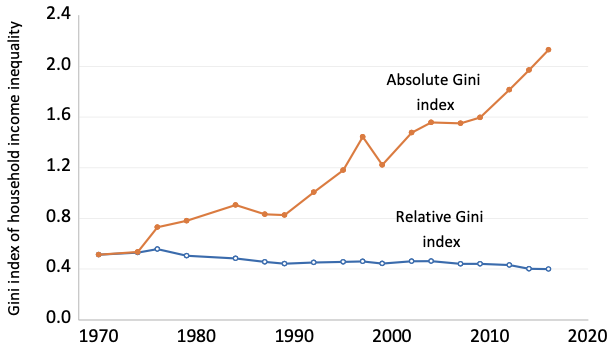
Ethnic Inequality And Poverty In Malaysia Since May 1969 Vox Cepr Policy Portal
Multidimensional Poverty Measure

Articles Persuasive Essay Topics In 2021 Persuasive Essays Essay Writing Essay

It Just Takes Rm900 A Month To Lift Urban Poor Out Of Absolute Poverty The Edge Markets
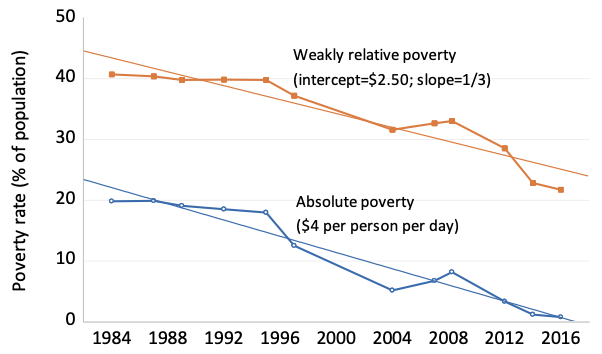
Ethnic Inequality And Poverty In Malaysia Since May 1969 Vox Cepr Policy Portal
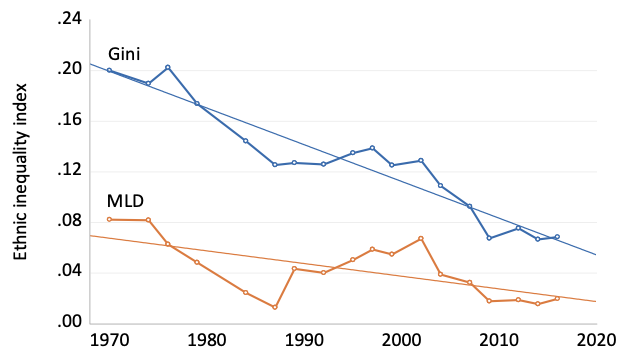
Ethnic Inequality And Poverty In Malaysia Since May 1969 Vox Cepr Policy Portal

Poverty In East Asia And Southeast Asia Upper Middle Income Countries World Data Lab
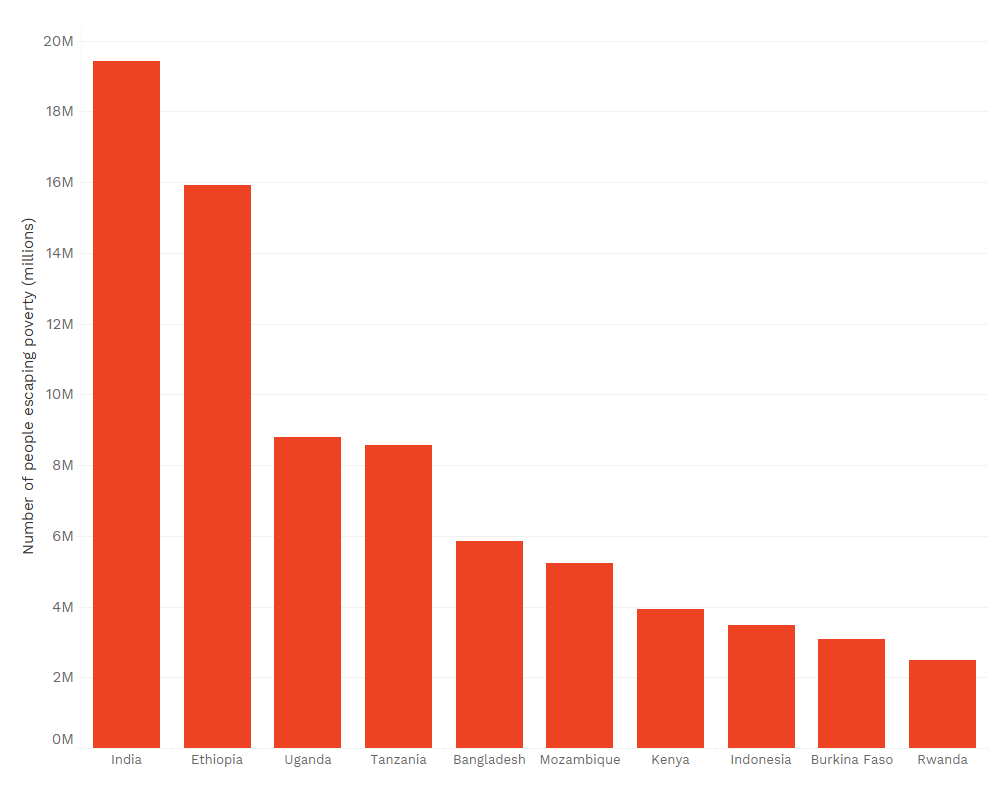
To Move The Needle On Ending Extreme Poverty Focus On Rural Areas

What Is Poverty And Its Different Types

The Connection Between Poverty And The Economy Federal Reserve Bank Of Minneapolis

/PovertyThresholdsfor2020bySizeofFamilyandNumberofRelatedChildrenUnder18YearsUPDATED-0a4a5e35abef4318998e13e6d987ffd7.jpg)


